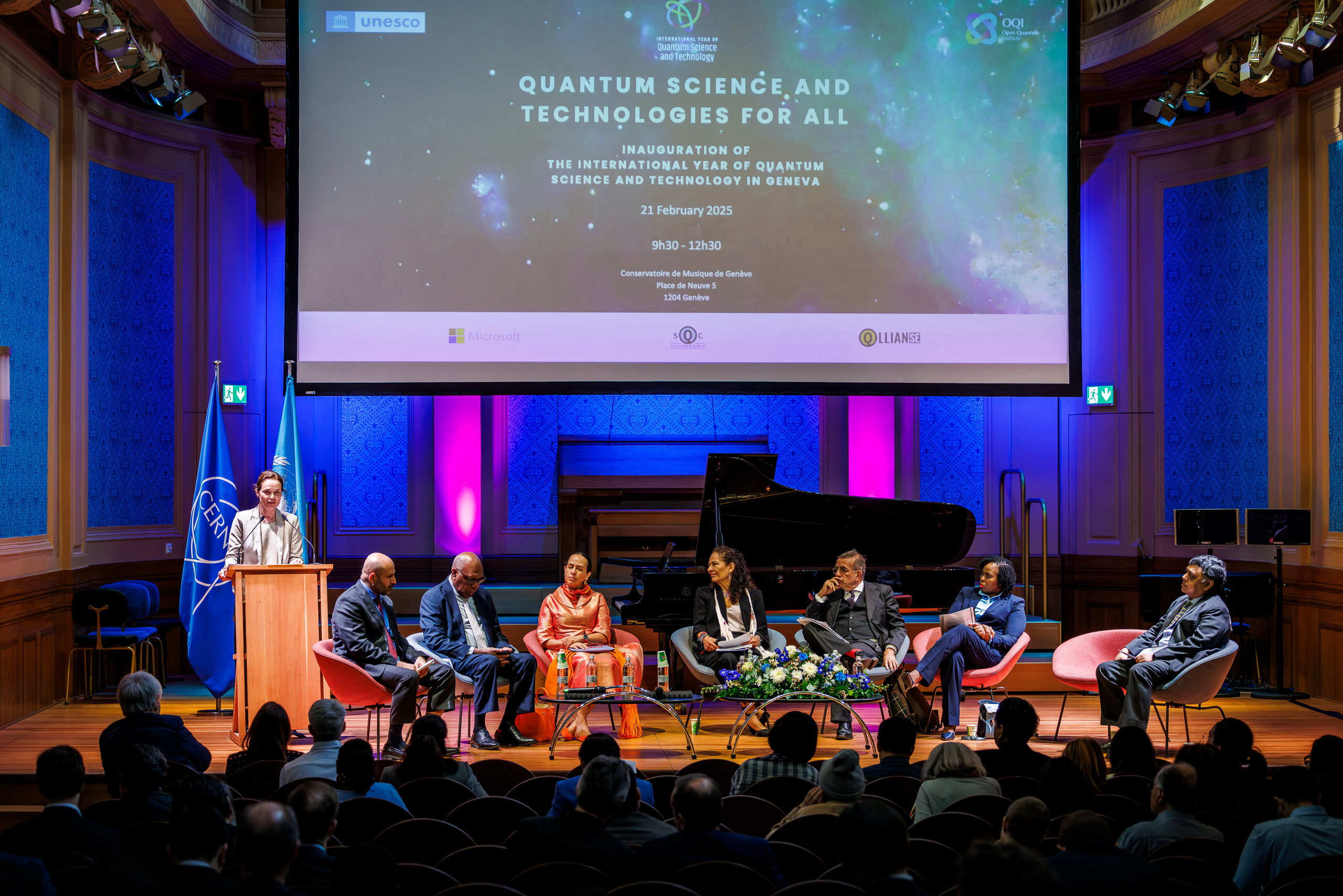
This December, I attended the Quantum Education Summit in Barcelona, Spain. The three-day conference was packed with talks, panels, workshops, and featured people and projects related to teaching and learning quantum science.
By the end, my head was spinning with thoughts of the future; the burgeoning field of quantum education is transforming the way the world engages with quantum science and technology, and STEM education as a whole.
Here are the top five takeaways you’ll need heading into 2026.

Takeaway #1: Everybody has a part to play
Quantum education is not defined by industry, job title, or continent, but by the intersection of quantum science and technology with society.
The string running through the 40+ talks was diversity in execution and unity of purpose: everyone approached quantum education from a different angle, but with the same goal in mind. Aggie Branczyk, from Quantum Salon in Waterloo, Canada, presented a communication framework for quantum tech start-ups, while Kirsten Stadermann, a professor at the University of Twente in the Netherlands, introduced a workshop for high school teachers. Paraskevi Ganoti, a policy officer from the European Commission, brought up both policy and strategy for quantum technology in Europe, while Jun Hao Hue, an education outreach manager at the Center for Quantum Technologies in Singapore, followed up with a talk on QCamp, a week-long quantum camp for kids. Every unique perspective reminded the audience that quantum science and technology do not belong to one sector in one continent—they belong to all of us. The future of quantum education depends on putting our heads together.
Takeaway #2: Hands-on experiences are essential
People want to get their hands on quantum—literally. Once upon a time, education was textbooks and lecture halls; now it is board games, DIY experiments, and handheld, glowing qubits.
The highlights from across the conference would have to include the showcase of tangibles. You couldn’t miss John Donahue’s suitcase full of easy-to-make quantum experiments for high school students—a senior scientific outreach manager at the Institute for Quantum Computing in Waterloo, Canada. John Donahue showed what quantum experiments for students are possible. From Palo Alto, California, and founder of Qolour, Sohum Thakkar’s colorful, handheld Qubis became an iconic symbol of what hands-on experimentation could really mean. Even inside the classroom, educators have taken game play seriously: Bjarke Takashi Røjle Christensen from the NNF Quantum Computing Programme and Copenhagen, Denmark, showed us how he uses light and optical fibers to transform his quantum physics class into a spy mission.
There are numerous excellent resources for learning quantum, but the ones that stood out were the ones we could hold in our hands.
Takeaway #3: Quantum education is creative
Quantum science challenges us to think outside the box to understand what’s inside it; quantum education is one of the areas transforming what we consider the box itself.
School is not the only place to learn, and this idea was evident in the meeting—it was bursting with a plethora of online classes, games, webinars, and resources for students and civilians alike. Araceli Venegas-Gomez’s company, Qureca, based in Barcelona, shares online courses, board games, and other resources to make sure everybody can learn quantum. Bob Coecke, creator of quantum pictorialism and chief scientist at Quantinuum, has a book, “Quantum in Pictures,” to teach whoever picks it up about quantum computing through pictures alone. Platforms like Q-CTRL Black Opal and IBM’s Quantum even make it possible to practice programming quantum computers completely online.
Quantum education is leaning into learning and embracing questions about education, such as where it takes place and how it’s done. The best part? It’s changing who gets to engage in it too.
Takeaway #4: Impacts will come from everywhere
“Talent is everywhere; opportunity is not.”
Ebony Heart
Leaders around the world are ensuring quantum education gives everyone a chance to contribute.
Henry Martin, lecturer at Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology and coordinator at RealMaths, is one such leader from Ghana. His talk emphasized using quantum science and technology to encourage inclusivity. It was an excellent foreshadowing for the closing ceremony of IYQ in Accra, where Yaseera Ismail (a Quantum 100 recipient) and senior lecturer at Stellenbosch University will be speaking as well. Her talk in Barcelona shared success stories around building a quantum ecosystem in South Africa, and the quantum communication link that put her lab on the quantum map. Finally, Eboney Hearn, executive director at MIT and the source of this section’s opening quote, shared details about MIT’s MITES program and how her team used outreach to visit students in underrepresented neighborhoods and bring them to Boston to study STEM.
Quantum education is mapping uncharted territory. There are more opportunities than ever for students, professors, and professionals to mark their place.

Takeaway #5: Building bridges matters
Collaboration—across countries, industries, and initiatives—is the key to quantum education. If there is one thing I walked away with from this conference, it was that working together means more than just being in the same room: we need to work to understand each other too.
Heather Lewandoski, professor and faculty director of CUbit Quantum Initiative at the University of Colorado, Boulder , gave the presentation that stood out to me the most. Her approach toward quantum education built a bridge between academia, industry, and students. She understood what students wanted (real, applicable skills), what industry needed (a quantum workforce), and built the bridge between them. Her capstone research class at the University of Colorado, Boulder, has students dedicate one year of research to solving the local quantum industry’s problems. The result? A trained workforce confident in their abilities, doing research for local quantum companies. A win-win.
The world is already separated by language, industries, fields, occupations, motivations, and oceans. The quantum education summit showed us how we can use quantum education to build bridges between them.
That’s what I’m hoping to see in 2016.
While the International Year of Quantum Science and Technology is coming to an end in February, its impact will not end there.
Here’s to the next 100 years.

Serena Krejci-Papa is a first-year master’s student at the University of Barcelona, studying theoretical and computational chemistry with the Erasmus Mundus program. She writes about complex science topics in a way that makes people laugh. You can find more about her at Sciencewithserena.com.